Last updates June 3, 1999
![]()
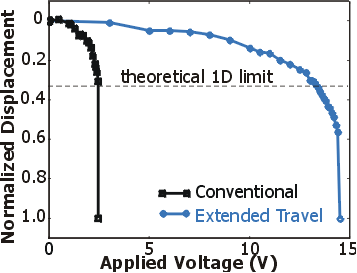
Conventional electrostatic micromechanical actuators can only travel one-third of the initial gap stably. By increasing the effective gap through the introduction of a capacitor in series, the stable travel range can be extended. However, parasitic capacitances must be minimized. The "folded capacitor" design achieves this with minimal changes to a conventional layout. Measurements show that the concept works but is ultimately limited by a tilting instability.
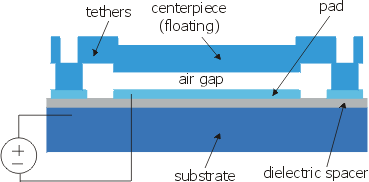
The device consists of a centerpiece suspended by flexible tethers. These components are electrically isolated from the electrical connections by dielectric spacers. Parasitic capacitances, which limit the stable travel range, are minimized.
Folded capacitor cross-section
The fabricated device can travel almost twice the conventional range before succumbing to a tilting instability. When the centerpiece tilts and lands on its side, the capacitive voltage division required for stable travel fails.
3D view of device
Travel distance measurement