


Next: TR/BDF2
Up: Generalized Trapezoid Family
Previous: Rate form
The generalized trapezoid algorithm provides access to three
specific timestepping methods depending on the value of 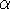 :
forward Euler (
:
forward Euler ( 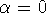 ), trapezoid rule (
), trapezoid rule ( 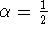 ), and backward Euler (
), and backward Euler ( 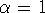 ).
).
- Any method with
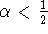 is conditionally
A-stable; time-steps are constrained by the maximum eigenvalue of the
discretized system. Arbitrarily large time-steps will produce an
amplification matrix with entries larger than 1 in magnitude. This
can lead to incorrect exponential growth in the solution.
is conditionally
A-stable; time-steps are constrained by the maximum eigenvalue of the
discretized system. Arbitrarily large time-steps will produce an
amplification matrix with entries larger than 1 in magnitude. This
can lead to incorrect exponential growth in the solution. - The trapezoid rule (
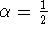 ) is second order
accurate in time. All other values of
) is second order
accurate in time. All other values of 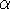 produce first order
methods.
produce first order
methods. - Backward Euler (
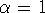 ) is the only method that is both
A-stable and L-stable. With
) is the only method that is both
A-stable and L-stable. With 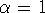 , the entries in the
amplification matrix are bounded by [0,1] (L-stable). Other
values of
, the entries in the
amplification matrix are bounded by [0,1] (L-stable). Other
values of 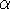 (
( 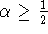 ) can produce
amplification matrices with values near -1 leading to
solutions with oscillatory behavior.
) can produce
amplification matrices with values near -1 leading to
solutions with oscillatory behavior.
Dan Yergeau
Wed Aug 20 14:01:54 PDT 1997
![]() :
forward Euler (
:
forward Euler ( ![]() ), trapezoid rule (
), trapezoid rule ( ![]() ), and backward Euler (
), and backward Euler ( ![]() ).
).